mysql必知必会笔记(1)
数据库定义:数据库是一个以某种有组织的方式存储的数据集合。
表:表是一种结构化的文件,可用来存储某种特定类型的数据。
模式:表具有一些特性,这些特性定义了数据在表中如何存储,如可以存 储什么样的数据,数据如何分解,各部分信息如何命名,等等。描述表 的这组信息就是所谓的模式,模式可以用来描述数据库中特定的表以及 整个数据库(和其中表的关系)。
列:表中的一个字段。所有表都是由一个或多个列组 成的。
行:表中的数据是按行存储的,所保存的每个记录存储在自己的行内。
主键:表中每一行都应该有可以唯一标识自己的一列(或一组列)。
主键是用来标识出唯一的行,如果没有主键,那么涉及到相关操作的时候,就有可能无法保证删除到正确的行。
- 设置主键
CREATE TABLE student_score ( number INT, subject VARCHAR(30), score TINYINT, PRIMARY KEY (number, subject) );1
2
3
4
5
6
# 主键设置规则
任意两行都不具有相同的主键值;
每个行都必须具有一个主键值(主键列不允许NULL值)
不更新主键列中的值;
不重用主键列的值;
不在主键列中使用可能会更改的值。(例如,如果使用一个
名字作为主键以标识某个供应商,当该供应商合并和更改其
名字时,必须更改这个主键。)
# MySQL
数据的所有存储、 检索、管理和处理实际上是由数据库软件——DBMS(数据库管理系统) 完成的。MySQL是一种DBMS,即它是一种数据库软件。注意DBMS和数据库的概念完全不同
# 有用的命令行
SHOW COLUMNS FROM 表名 列出表里所有的列 做代码生成器的时候可以用到
DESCRIBE 表名 列出表里所有的列 同上
SHOW STATUS,用于显示广泛的服务器状态信息;
SHOW CREATE DATABASE和SHOW CREATE TABLE,分别用来显示创建特定数据库或表的MySQL语句;
SHOW GRANTS,用来显示授予用户(所有用户或特定用户)的安
全权限;
SHOW ERRORS和SHOW WARNINGS,用来显示服务器错误或警告消息。
mysql -h主机名 -u用户名 -p密码 连接数据库注意-p和密码之间没有空格
退出:
quit
exit
\q
2
3
# 查询
DISTINCT 排重关键字
SELECT DISTINCT vend_idF FROM products SELECT DISTINCT vend_id,prod_price FROM `products`1
2注意这个DISTINCT关键字作用与后面所有的列,后面跟着的所有列都一样才合并为一行,否在将分开显示
limit 限制返回行数
select prod_name from products limit 5,5; #从第 6 行开始,检索 5 行 select prod_name from products limit 4 OFFSET 3; #从第 3 行开始,检索 4 行1
2注意从mysql5.5之后新增了offset字段,目的是增强语义化。还有行数是从0开始的,limit5取得是第六行
使用完全限定的表名
select products.prod_name from crashcourse.products;1排序 使用order by进行排序,默认asc升序排序,desc降序排序
select prod_id, prod_price,prod_name from products order by prod_price desc, prod_name desc; #先按价格降序排列,再按产品名降序排列1
2
3查询价格最高的商品(如果价格一样就有问题),这个句子展示了limit必须在order by后面
select prod_price from products order by prod_price desc limit 1; # 最高值1where 过滤数据
使用where字段过滤数据,除了常见的判断符,还有<>符号,表示不等select vend_id,prod_name from products where vend_id <> 1003; # 检索不是由1003供应商制造的所有产品1还有between范围值检查和null字符检查,这两个都用的少,注意这个is null,在数据库中null和''和0是由区分的,查询is null 那一列必须是null值
select prod_name,prod_price from products where prod_price between 5 and 10; # 价格 大于等于5,小于等于10 的产品名、产品价格1select prod_name from products where prod_price is null; # 返回prod_price为空值null的prod_name,无对应数据1and 和 or
使用and和or进行where子句连接,但要注意,同时使用and,or时,查询是由顺序的,必须使用()将子句包裹起来。select prod_name,prod_price from products where vend_id = 1002 or vend_id = 1003;1in 和 not
inselect prod_name,prod_price from products where vend_id in (1002,1003) order by prod_name;1
2not
select prod_name,prod_price from products where vend_id not in (1002,1003) order by prod_name; # Mysql支持not对in,between,exsits子句取反1
2
3
# 搜索
通配符搜索
使用%和_进行通配符搜索,%匹配多个字符,_匹配一个字符,使用like匹配字段中包含anvil,并且anvil出现的次数不受限制。select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like "%anvil%";1注意 % 不能匹配null值,并且将%放在句首将会拖慢搜索速度
正则表达式匹配 mysql中也可以使用正则匹配,但是对于正则表达式的支持比较有限,这里只记录书中出现的
在正则表达式中,匹配任意 一个 字符
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp ".000";1正则表达式匹配默认不分大小写,需使用BINARY区分大小写
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp binary "JetPack .000";1正则表达式的OR操作符: |
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp "1000|2000" order by prod_name;1正则表达式匹配几个字符之一 [ ]
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[123] Ton' order by prod_name; # [123]匹配单一字符:1或2或31正则表达式匹配范围
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[1-5] Ton' order by prod_name; # [1-5]匹配1,2,3,4,51正则表达式匹配特殊字符,必须用\前导,进行转义 多数正则使用单反斜杠转义,但mysql使用双反斜杠,mysql自己解释一个,正则表达式库解释一个
select vend_name from vendors where vend_name regexp "\\." order by vend_name; # ‘\\.'匹配字符.1正则表达式匹配字符类
[:alnum:] 任意字母和数字(同[a-zA-Z0-9]) [:alpha:] 任意字符(同[a-zA-Z])
[:blank:] 空格和制表(同[\t])
[:cntrl:] ASCII控制字符(ASCII 0到31和127)
[:digit:] 任意数字(同[0-9])
[:graph:] 与[:print:]相同,但不包括空格 [:lower:] 任意小写字母(同[a-z])
[:print:] 任意可打印字符 [:punct:] 既不在[:alnum:]又不在[:cntrl:]中的任意字符 [:space:] 包括空格在内的任意空白字符(同[\f\n\r\t\v])
[:upper:] 任意大写字母(同[A-Z])
[:xdigit:] 任意十六进制数字(同[a-fA-F0-9])select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[:digit:]' order by prod_name; #[:digit:]匹配任意数字1匹配多个实例 mysql正则中对于多个重复字符的支持
select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '\\([0-9] sticks?\\)' order by prod_name; # 返回了'TNT (1 stick)'和'TNT (5 sticks)'1
2定位符

select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '^[0-9\\.]' order by prod_name; #找出以一个数(包括以小数点开始的数)开始的所有产品 select prod_name from products where prod_name regexp '[0-9\\.]' order by prod_name; #找出包括小数点和数字的所有产品1
2
# 函数
拼接字段 concat()
select concat(vend_name,' (',vend_country,')') from vendors order by vend_name;1删除空格
删除数据左侧多余空格 ltrim()
删除数据两侧多余空格 trim()
删除数据右侧多余空格 rtrim()select concat(rtrim(vend_name),' (',rtrim(vend_country),')') from vendors order by vend_name;1as赋予别名
select concat(rtrim(vend_name),' (',rtrim(vend_country),')') as vend_title from vendors order by vend_name;1执行算数计算
select prod_id,quantity,item_price from orderitems where order_num = 20005;1文本函数
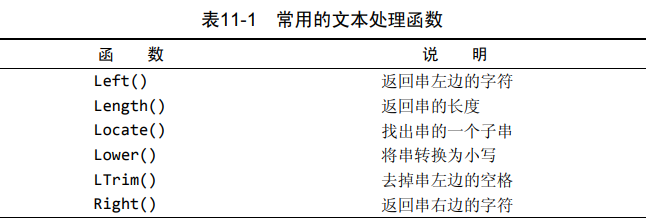

select vend_name, upper(vend_name) as vend_name_upcase from vendors order by vend_name;1soundex() 描述语音表示的字母数字模式的算法,对串按照发音比较而不是字母比较
select cust_name,cust_contact from customers where cust_contact = 'Y. Lie'; # 无返回 select cust_name,cust_contact from customers where soundex(cust_contact) = soundex('Y. Lie'); # 按发音搜索1
2日期函数
常用日期函数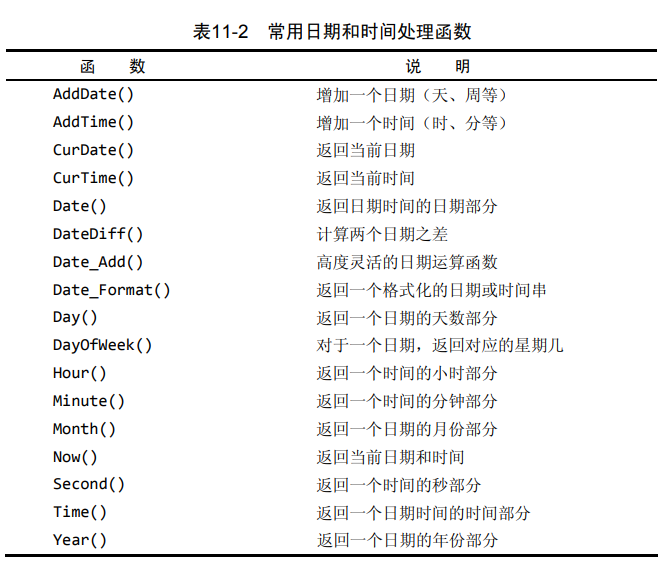
按照date()日期进行过滤信息,更可靠select cust_id,order_num from orders where date(order_date) = "2005-09-01";1聚合函数
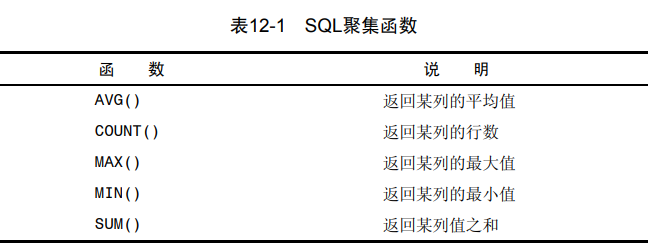 avg() 求和,忽略null
avg() 求和,忽略nullselect avg(prod_price) as avg_price from products;1count() 对行的数目进行统计 忽略null
select count(*) as num_cust from customers;1max() & min() 最大最小
select max(prod_price) as max_price from products; select min(prod_price) as min_price from products;1
2在用于文本数据时,如果数据按相应的列排序,则MIN()返回最前面一行
select min(prod_name) from products;1sum 求和
select sum(quantity) as items_ordered from orderitems;1使用聚合函数时去重
select avg(distinct prod_price) as avg_price from products where vend_id = 1003;1在使用COUNT的使用指定条件,最后必须加上NULL,因为COUNT是不计算null的,如果这行数据的release_year不等于2006,那么就是返回null,而null不被计算,所以用这种方式进行筛选
count(release_year = '2006' or NULL)1
# 分组函数
- ROLLUP关键字
使用WITH ROLLUP关键字,可以得到每个分组的汇总值,下述语句得到所有分组count(*)的和14查询结果,3+2+7+2 = 14select vend_id, count(*) as num_prods from products group by vend_id with rollup;1值得注意的是,这个rollup可以配合coalesce函数其别名1001 3 1002 2 1003 7 1005 2 141
2
3
4
5 - coalesce函数
coalesce(a,b,c); 参数说明:如果a==null,则选择b;如果b==null,则选择c;如果a!=null,则选择a;如果a b c 都为null ,则返回为null(没意义)。查询结果:select coalesce(vend_id,"总供应商"), count(*) as num_prods from products group by vend_id with rollup;11001 3 1002 2 1003 7 1005 2 总供应商 141
2
3
4
5 - having
和having组合使用select vend_id,count(*) as num_prods from products where prod_price >=10 group by vend_id having count(*)>=2;1
# 子查询
- 作为计算字段使用子查询
select cust_name,cust_state, (select count(*) from orders where orders.cust_id = customers.cust_id) as orders from customers order by cust_name;1
2
# 连接表
- 联结
使用where字句联结两张表,这种使用where的方式,会去匹配每一个where中条件select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from vendors,products where vendors.vend_id = products.vend_id order by vend_name,prod_name;1
2
3
4 - 内部联结
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from vendors inner join products on vendors.vend_id = products.vend_id;1
2
3
# 高级连接
表别名
select cust_name,cust_contact from customers as c,orders as o,orderitems as oi where c.cust_id = o.cust_id and oi.order_num = o.order_num and prod_id = 'TNT2';1
2
3
4
5自联结
select p1.prod_id,p1.prod_name from products as p1, products as p2 where p1.vend_id = p2.vend_id and p2.prod_id = 'DTNTR';1
2
3
4自然联结 方法:通过对表使用通配符*,对所有其他表的列使用明确的子集,自然联结使每个列只返回一次
select c.*,o.order_num,o.order_date,oi.prod_id,oi.quantity,oi.item_price from customers as c,orders as o,orderitems as oi where c.cust_id = o.cust_id and oi.order_num = o.order_num and prod_id = 'FB';1
2
3
4
5外部联结 方法: 内部联结,这里的内部联结感觉取一个交集的感觉,里面的列必须是双方都有的。
select customers.cust_id,orders.order_num from customers inner join orders on customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id;1
2
3左外部联结 左外部联结,跟上一个内部联结放在一起谈,左外部联结更像以左边表的列为主体,去找右边的能够对应的数据
select customers.cust_id,orders.order_num from customers left outer join orders on customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id;1
2
3右外部联结 右联结与左联结相反,我发现这个联结这个词用得很恰当,因为本质是集合操作,没有多余的思想。
select customers.cust_id,orders.order_num from customers right outer join orders on customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id;1
2
3带聚集函数的联结
select customers.cust_name, customers.cust_id, count(orders.order_num) as num_ord from customers inner join orders on customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id group by customers.cust_id;1
2
3
4
5
6select customers.cust_name, customers.cust_id, count(orders.order_num) as num_ord from customers left outer join orders on customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id group by customers.cust_id;1
2
3
4
5
6
# 组合查询
使用union
select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where prod_price <=5 union select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002);1
2
3union在一张表的时候也可以用where来代替,但是使用多表的话,union感觉更好做一点。
union all
select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where prod_price <=5 union all select vend_id,prod_id,prod_price from products where vend_id in (1001,1002);1
2
3
# 全文搜索
match和against
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('rabbit');1显示
select note_text, match(note_text) against('rabbit') as 'rank' from productnotes;1查询扩展
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('anvils' with query expansion);1布尔搜索 用来更灵活筛选全文搜索的结果
布尔操作符 说明 + 包含,词必须存在 - 排除,词必须不出现 > 包含,而且增加等级值 < 包含,且减少等级值 () 把词组成子表达式(允许这些表达式作为一个组被包含、排除、排列等) ~ 取消一个词的排序值 * 词尾的通配符 “ ” 定义一个短语(与单个词的列表不一样,它匹配整个短语一边包含或排除这个短语)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9全文本搜索检索包含词heavy的所有行 关键字IN BOOLEAN MODE,实际上没有指定布尔操作符,其结果与没有指定布尔方式的结果相同
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('heavy' in boolean mode);1-rope* 排除包含rope*(任何以rope开始的词,包括ropes)的行
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('heavy -rope*' in boolean mode);1匹配包含词rabbit和bait的行
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('+rabbit +bait' in boolean mode);1不指定操作符,搜索匹配包含rabbit和bait中的至少一个词的行
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('rabbit bait' in boolean mode);1搜索匹配短语rabbit bait而不是匹配两个词rabbit和bait。
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('"rabbit bait"' in boolean mode);1匹配rabbit和carrot,增加前者的等级,降低后者的等级
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('>rabbit <carrot' in boolean mode);1必须匹配词safe和combination,降低后者的等级
select note_text from productnotes where match(note_text) against('+safe +(<combination)' in boolean mode);1
# 插入
单个插入 插入的时候指定列名
insert into customers (cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country,cust_contact,cust_email) values ('Pep E. LaPew','100 Main Street','Los Angeles','CA','90046','USA',NULL,NULL);1
2批量插入
# 方法一:多个insert的语句 insert into customers(cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country) values('Pep E. LaPew','100 Main Street','Los Angeles','CA','90046','USA'); insert into customers(cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country) values('M. Martian','42 Galaxy Way','New York','NY','11213','USA');1
2
3
4
5# 方法二:多个insert的语句 insert into customers(cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country) values('Pep E. LaPew','100 Main Street','Los Angeles','CA','90046','USA'),('M. Martian','42 Galaxy Way','New York','NY','11213','USA');1
2
3insert selec 插入查询出来的值
insert into customers (cust_contact,cust_email,cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country) select cust_contact,cust_email,cust_name,cust_address,cust_city,cust_state,cust_zip,cust_country from custnew;1
2
# 更新和删除
更新
UPDATE customers SET cust_name = 'The Fudds', cust_email = 'elmer@fudd.com' WHERE cust_id = 10005;1
2
3
4删除
delete from customers where cust_id = 10006;1如果想从表中删除 所有行,不要使用DELETE,可使用TRUNCATE TABLE语句 TRUNCATE实际是删除原来的表并重新创建一个表,而不是逐行删除表中的数据
# 表操作
新建表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS customers ( cust_id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, cust_name char(50) NOT NULL , cust_address char(50) NULL , cust_city char(50) NULL , cust_state char(5) NULL , cust_zip char(10) NULL , cust_country char(50) NULL , cust_contact char(50) NULL , cust_email char(255) NULL , PRIMARY KEY (cust_id) ) COMMENT '表的注释信息', ENGINE=InnoDB;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14添加列 给vendors表增加一个名为vend_phone的列
alter table vendors add vend_phone char(20);1
2添加列到指定位置
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD COLUMN 列名 列的类型 [列的属性] FIRST;1添加列到指定列后
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD COLUMN 列名 列的类型 [列的属性] AFTER 指定列名;1删除列
alter table vendors drop column vend_phone;1
2修改列
ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY 列名 新数据类型 [新属性];1列的默认值
列名 列的类型 DEFAULT 默认值1设置非空列
列名 列的类型 NOT NULL1列设置数据不重复 在设置列的时候可以使用unique关键字,保证列中数据不会重复。
id_number CHAR(18) UNIQUE,1也可以单独设置
UNIQUE KEY [约束名称] (列名1, 列名2, ...)1定义外键
ALTER TABLE orderitems ADD CONSTRAINT fk_orderitems_orders FOREIGN KEY (order_num) REFERENCES orders (order_num);1删除表
drop table customers2;1重命名表
//第一种 rename table backup_customers to customer, backup_vendors to vendors, backup_products to products; //第二种 ALTER TABLE 旧表名 RENAME TO 新表名;1
2
3
4
5
6转移表到另一个数据库
ALTER TABLE first_table1 RENAME TO dahaizi.first_table1;1多个操作合并
ALTER TABLE 表名 操作1, 操作2, ..., 操作n;1
# 视图操作
- 创建视图
create view productcustomers as select cust_name,cust_contact,prod_id from customers,orders,orderitems where customers.cust_id = orders.cust_id and orders.order_num = orderitems.order_num;1
2
3
4
5
# 存储过程
- 创建存储过程
delimiter //表明使用//作为语句的结尾符,因为使用;在命令行状态下会报错
delimiter // create procedure productpricing() begin select avg(prod_price) as priceaverage from products; end1
2
3
4
5 - 调用存储过程
call productpricing();1 - 删除存储过程
drop procedure productpricing;1 - 使用参数out
调用存储过程并不会直接返回数据,必须传入out参数,将结果赋值out参数
delimiter // create procedure productpricing(out pl decimal(8,2), out ph decimal(8,2), out pa decimal(8,2)) begin select min(prod_price) into pl from products; select max(prod_price) into ph from products; select avg(prod_price) into pa from products; end //1
2
3
4
5
6
7call productpricing(@pricelow,@pricehigh,@priceaverage); select @pricehigh,@pricelow,@priceaverage;1
2 - 参数值in 额out
in参数代表传入值和out相反
delimiter // create procedure ordertotal( in onumber int, # onumber定义为IN,因为订单号被传入存储过程 out ototal decimal(8,2) # ototal为OUT,因为要从存储过程返回合计 ) begin select sum(item_price*quantity) from orderitems where order_num = onumber into ototal; end //1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10call ordertotal(20009,@total); select @total;1
2 - 复杂存储过程调用
delimiter // create procedure ordertotal( in onumber int, in taxable boolean, out ototal decimal(8,2) ) comment 'obtain order total, optionally adding tax' begin -- declare variable for total 定义局部变量total declare total decimal(8,2); -- declare tax percentage 定义局部变量税率 declare taxrate int default 6; -- get the order total 获得订单合计 SELECT SUM(item_price * quantity) FROM orderitems WHERE order_num = onumber INTO total; -- is this taxable? 是否要增加营业税? if taxable then -- Yes,so add taxrate to the total 给订单合计增加税率 select total+(total/100*taxrate) into total; end if; -- and finally,save to out variable 最后,传递给输出变量 SELECT total INTO ototal; END //1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23# 调用上述存储过程,不加税 call ordertotal(20005,0,@total); select @total; # 调用上述存储过程,加税 call ordertotal(20005,1,@total); select @total;1
2
3
4
5
6 - 存储过程信息
# 获得包括何时、由谁创建等详细信息的存储过程列表 # 该语句列出所有存储过程 show procedure status; # 过滤模式 show procedure status like 'ordertotal';1
2
3
4
5
# 使用游标
感觉这个游标只是说可以把一些业务操作放到数据库里,其他的作用还没看到
- 创建游标
delimiter // create procedure processorders() begin -- decalre the cursor 声明游标 declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders; -- open the cursor 打开游标 open ordernumbers; -- close the cursor 关闭游标 close ordernumbers; end //1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 - 使用游标
delimiter // create procedure processorders() begin -- declare local variables 声明局部变量 declare o int; -- decalre the cursor 声明游标 declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders; -- open the cursor 打开游标 open ordernumbers; -- get order number 获得订单号 fetch ordernumbers into o; /*fetch检索 当前行 的order_num列(将自动从第一行开始)到一个名为o的局部声明变量中。 对检索出的数据不做任何处理。*/ -- close the cursor 关闭游标 close ordernumbers; END //1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 触发器
- 创建触发器
create trigger newproduct after insert on products for each row select 'product added' into @new_pro; # mysql 5.0以上版本在TRIGGER中不能返回结果集,定义了变量 @new_pro; insert into products(prod_id,vend_id,prod_name,prod_price) values ('ANVNEW','1005','3 ton anvil','6.09'); # 插入一行 select @new_pro; # 显示Product added消息1
2
3
4 - 删除触发器
drop trigger newproduct;1 - 使用触发器
# insert触发器 create trigger neworder after insert on orders for each row select new.order_num into @order_num; insert into orders(order_date,cust_id) values (now(),10001); select @order_num;1
2
3
4 - delete触发器
delimiter // create trigger deleteorder before delete on orders for each row begin insert into archive_orders(order_num,order_date,cust_id) values(old.order_num,old.order_date,old.cust_id); # 引用一个名为OLD的虚拟表,访问被删除的行 end //1
2
3
4
5
6 - update触发器
# update触发器 # 在更新vendors表中的vend_state值时,插入前先修改为大写格式 create trigger updatevendor before update on vendors for each row set new.vend_state = upper(new.vend_state); # 更新1001供应商的州为china update vendors set vend_state = 'china' where vend_id =1001; # 查看update后数据,1001供应商对应的vend_state自动更新为大写的CHINA select * from vendors;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 事务管理
基本概念
- 事务 transaction 指一组sql语句
- 回退 rollback 指撤销指定sql语句的过程
- 提交 commit 指将未存储的sql语句结果写入数据库表
- 保留点 savepoint 指事务处理中设置的临时占位符,可以对它发布回退(与回退整个事务处理不同)
事务操作
-- 控制事务处理 # 开始事务及回退 select * from ordertotals; # 查看ordertotals表显示不为空 start transaction; # 开始事务处理 delete from ordertotals; # 删除ordertotals表中所有行 select * from ordertotals; # 查看ordertotals表显示 为空 rollback; # rollback语句回退 select * from ordertotals; # rollback后,再次查看ordertotals表显示不为空 # commit 提交 start transaction; delete from orderitems where order_num = 20010; delete from orders where order_num = 20010; commit; # 仅在上述两条语句不出错时写出更改 # savepoint 保留点 # 创建保留点 savepoint delete1; # 回退到保留点 rollback to delete1; # 释放保留点 release savepoint delete1;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 全球化和本地化
- 字符集和校对顺序
查看所支持的字符集完整列表查看所支持校对的完整列表,以及它们适用的字符集
show character set;1确定所用系统的字符集和校对show collation;1指定字符集show variables like 'character%'; show variables like 'collation%';1
2除了能指定字符集和校对的表范围外,MySQL还允许对每个列设置它们create table mytable ( column1 int, column2 varchar(10) ) default character set hebrew collate hebrew_general_ci;1
2
3
4
5
6查询时指定顺序create table mytable ( column1 int, column2 varchar(10), column3 varchar(10) character set latin1 collate latin1_general_ci )default character set hebrew collate hebrew_general_ci;1
2
3
4
5
6
7select * from customers order by lastname,firstname collate latin1_general_cs;1
# 安全管理
- 管理用户
use mysql; select user from user;1
2 - 创建用户账户
创建用户设置密码重命名一个用户账户
create user ben identified by 'p@$$w0rd';1删除用户rename user ben to bforta;1查看赋予用户账号的权限drop user bforta;1操作权限show grants for bforta;1撤销权限grant select on crashcourse.* to bforta;1简化授权revoke select on crashcourse.* from bforta;1重新设置密码grant select,insert on crashcourse.* to bforta;1set password = 'n3w p@$$w0rd';1
# 数据库维护
- 分析表
analyze table orders;1 - 检查表是否存在错误
check table orders,orderitems; check table orders,orderitems quick; # QUICK只进行快速扫描1
2 - 优化表OPTIMIZE TABLE,消除删除和更新造成的磁盘碎片,从而减少空间的浪费
optimize table orders;1 - 删除数据库
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS 数据库名;1
